What Factors Influence the Consumption of Plant-Based Meat Alternatives and Their Nutritional Advantages? A Mixed Methods Study
Dec 12, 2024Explore factors influencing the consumption of plant-based meat alternatives (PBMAs), including production technology, nutritional profiles, and environmental impacts. Learn about consumer behavior, market trends, and potential safety and nutritional risks associated with PBMAs, highlighting their role in sustainable and health-conscious diets.
Factors Influencing the Consumption of Plant-Based Meat Alternatives and Their Nutritional Advantages: A Mixed Methods Study
Based on the provided search results, several factors influence the consumption of plant-based meat alternatives (PBMAs), and their nutritional advantages are a complex issue. The following points summarize the findings:
Production Technology and Nutritional Profiles
-
Production Technology: The production of PBMAs involves several stages: protein isolation and functionalization (often using soy, peas, fava beans, rapeseed, and hemp), product formulation (including colorants, flavorings, and fat/oil replacers), processing (most commonly extrusion), and storage. The choice of protein source and processing methods significantly impacts the final product's nutritional profile and sensory attributes. Extrusion, while efficient, can affect the protein's native structure. Alternative technologies like 3D printing and high-temperature shearing show promise but require further development.
-
Nutritional Profiles and Health Impacts: Nutritional variability among PBMAs is substantial. While some offer higher fiber and lower fat content compared to animal meat, others may be lower in protein or certain essential amino acids (like methionine). The bioavailability of micronutrients like iron also differs. Studies comparing diets with PBMAs to omnivorous diets highlight potential nutrient inadequacies (e.g., vitamin B12), especially when novel PBMAs are used. Long-term human intervention studies are needed to fully assess the health impacts. A study by Crimarco et al. found no improvement in inflammation biomarkers after plant-based meat consumption, highlighting the need for further research.
-
Environmental Impacts: Life Cycle Assessments (LCAs) suggest PBMAs can be more sustainable than animal products in terms of greenhouse gas emissions, land and water use, and biodiversity. However, the processing stage of PBMAs can significantly impact their overall environmental footprint. The use of energy from fossil fuels is a major concern, but alternative energy solutions could mitigate this. Further LCA studies are needed, particularly those using consistent methodologies and functional units.
Consumer Behavior and Market Analysis
-
Consumer Behavior: Sensory attributes (taste, texture, appearance) strongly influence consumer acceptance. Mimicking meat characteristics is a key marketing strategy, but the long list of ingredients in many PBMAs can raise concerns about processing and health. Product familiarity is also a significant factor. Studies show that flexitarians and those motivated by health and environmental concerns are more likely to accept PBMAs. Heavy meat eaters may be less willing to substitute. Price remains a barrier to wider adoption.
-
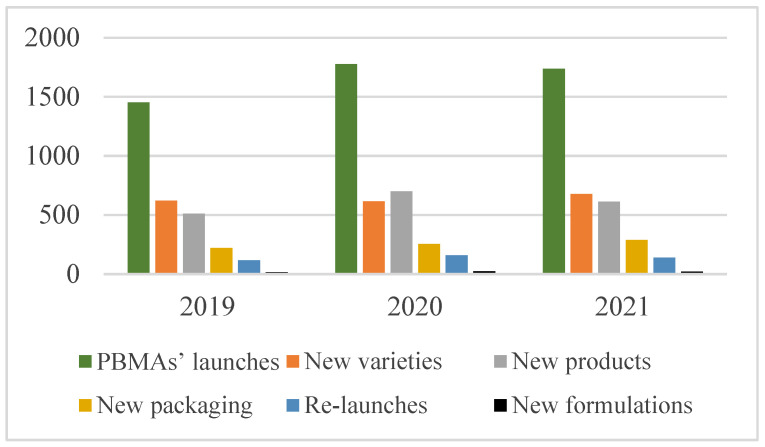
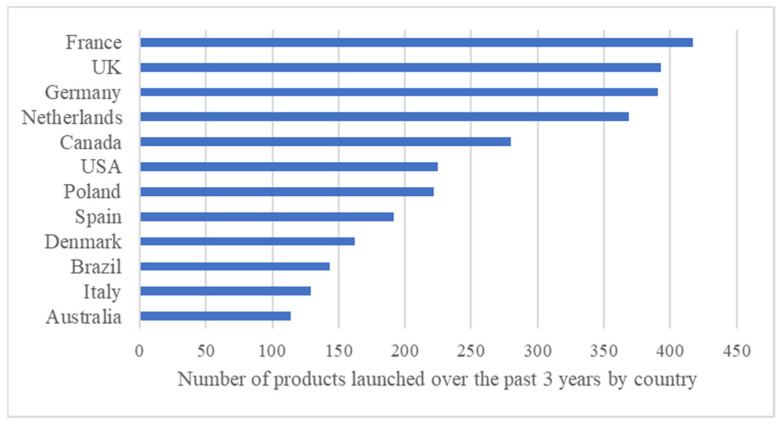
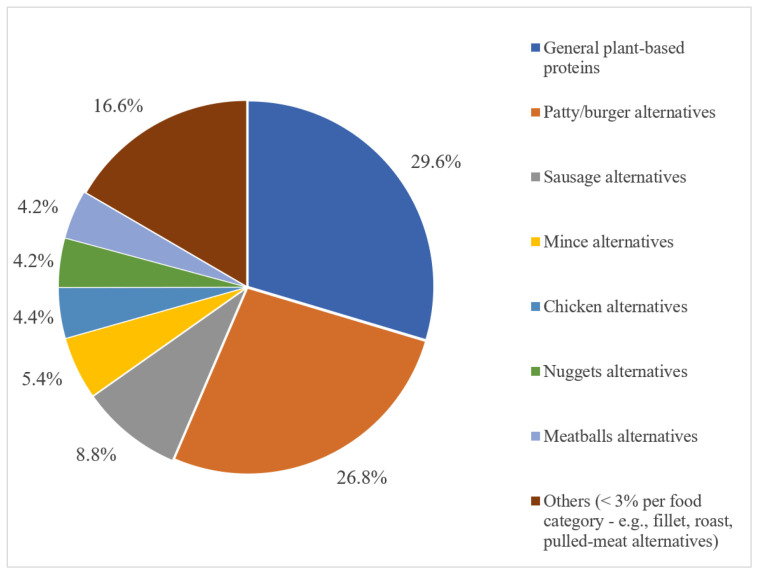
Market Analysis: The market for PBMAs is growing rapidly, particularly in Europe and North America. Burger/patty alternatives and general plant-based proteins are the most common categories. Soy-based components are the most frequently used ingredient. "Vegan/No Animal Ingredients" and "Plant Based" are the most common claims on packaging. Despite growth, the market share of PBMAs remains significantly smaller than that of the meat market, suggesting that PBMAs are often complementary to, rather than replacements for, animal-based products.
Safety and Nutritional Risks Associated with Plant-Based Meat Alternatives
A separate study examined safety and nutritional risks associated with PBMAs. Key findings include:
-
Allergens: Many plant proteins used in PBMAs (soy, pea, wheat) are known allergens. The use of genetically modified ingredients may introduce new allergy risks. Clear labeling is crucial.
-
Bacteria: While processing usually inactivates bacteria, some endospore-forming bacteria can survive. Post-processing contamination is also a concern.
-
Toxins: Mycotoxins (aflatoxins, ochratoxins, fumonisins) can contaminate raw ingredients. Natural toxins (lectins, cyanogenic glycosides) may also be present. The use of carrageenan raises some concerns about potential gastrointestinal issues, though more research is needed. Synthetic toxins (pesticide residues, hexane) are also potential hazards.
-
Thermally Induced Carcinogens: High-temperature processing can create carcinogens (heterocyclic aromatic amines, nitrosamines, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons).
-
Antinutrients: Legumes and other plant sources contain antinutrients that can reduce nutrient bioavailability.
-
Nutritional Profile: PBMAs show considerable variability in nutritional content. Some may be deficient in essential amino acids, vitamins, and minerals, while others may be high in saturated fat or sodium. Fortification strategies are employed, but their effectiveness and long-term health implications require further investigation. The highly processed nature of many PBMAs raises concerns about their overall health impact.


Jan 21, 2025
Explore the pros and cons of a plant-based diet, including health benefits, potential challenges, and tips for successful implementation. Learn about vegetarian, vegan, and flexitarian approaches.
Jan 20, 2025
Explore the latest research on plant-based diets and their powerful health benefits, including disease prevention, heart health, diabetes management, and cancer risk reduction.
Jan 16, 2025
Explore the nutritional landscape of processed fake meat, comparing them to traditional meat and whole plant foods. Learn about ingredients, health impacts, and making informed choices.